| Search | Statistics | User Listing | Forums |

| Mitsubishi 380 Forum -Exclusively for owners of the Australian 380 PS41 -> 380 Projects section -> Stayer's projects -> View Thread |
| ||
 | ||
|
| You are logged in as a guest. ( logon Only if you have registered by Email as per the instructions in the forum) |
 Turbo kit for 4G69 Turbo kit for 4G69Jump to page : 1 2 3 4 5 6 Now viewing page 1 [10 messages per page] | View previous thread :: View next thread |
| 380 Projects section -> Stayer's projects | Message format |
| stayer |
| ||
 Frequent flyer Gold Posts: 286       Location: Russia, Perm | Hi, guys! In this topic, I want to tell you about the turbo project. You may ask: "And how is supercharger?" I will answer. Supercharger very noisy. To me this is not much like it. Once on the American forum Galants, John said to me, make it the turbo. I think it's time to do it. I want to tell you how it's done, how to do a calculation and selection of components. I want to remind you, I don't know English, so I write through the electronic translator. Don't blame much, if something is not clear, you'd better ask about it. So, let's begin... | ||
| |||
| stayer |
| ||
 Frequent flyer Gold Posts: 286       Location: Russia, Perm | Many tuners built turbo, then calculated power and etc. However, this is not the right approach. Correctly first, calculate, and then to build the engine. There are a few simple points. 1) Initial settings. (what we have before construction) 2) the Desired result (the one that we want to get) 3) Calculation (we consider the air, fuel, power etc.) 4) Selection of the components (turbine, parts, etc.) 5) Installation (actually Assembly) 6) setup (ECU, pressure, fuel, etc.) That's it for this scheme will work. | ||
| |||
| stayer |
| ||
 Frequent flyer Gold Posts: 286       Location: Russia, Perm | 1)Initial settings. So, what we have? Engine code: 4G69 Size: 2.4 L (2378 QC) Cylinder: 87 mm Stroke: 100 mm Power: 160 HP. (117 kW) at 5750 rpm. with 158 ft·lbf (215 N·m) at 4000 rpm. Compression ratio : 9,5 MFI fuel injection, 4 valves per cylinder. Valves without the hydro-compensators. Automatic gearbox F4A4B. For the beginning of these parameters are sufficient. | ||
| |||
| stayer |
| ||
 Frequent flyer Gold Posts: 286       Location: Russia, Perm | 2) the Desired result. Oh, this item is always causes a lot of disputes. the voices of the people hundreds of horsepower. But not all people understand that they can use them. You can build any engine. And 400, and 500, and 1000 HP, etc. However, any increase shall entail significant spending. This relates primarily to the engine itself. Need to strengthen the pistons, rods, gear box, transmission, etc. The total amount of construction is increasing to infinity. Therefore, we must descend from the heavens to the earth and calculate what you can do. | ||
| |||
| stayer |
| ||
 Frequent flyer Gold Posts: 286       Location: Russia, Perm | If you leave the stock parts, we can boldly say - 100 HP per liter volume. Go back to step 1. The volume of 2378cc. Thus, the safe capacity will reach 238 hp. A further increase will require strengthening of the engine and the transmission. However, if the purpose of the project is to leave all part of the stock, then there is another option. This is the performance of the injectors. There are formulas for calculating the performance. They take into account the number of cylinders, pressure fuel pump, duty cycle,the losses of fuel (B.S.F.C.). However, I want to offer another, more simple way. If the duty cycle is equal to 90%, fuel rail pressure of 3 bar. The power can be calculated as: the Size of the injector : 5.25 x number of cylinders. Stock size GS injector = 275 cc. 275 : 5.25 x 4 = 209.5 Thus, the stock injectors, will be able to secure the capacity of 210 HP. That is, if you take the injectors for example from 6G75 = 305cc. 305 : 5.25 x 4 = 232 HP. | ||
| |||
| stayer |
| ||
 Frequent flyer Gold Posts: 286       Location: Russia, Perm | You think 210 HP is very little? Believe me, it will be a very fast car. Is much faster than a stock V6. Because it is important not only power as such. We must take into account the weight of the vehicle and a gear ratio gearbox. I stopped at the power of 210 HP. Now you need to make the calculation of the air. | ||
| |||
| stayer |
| ||
 Frequent flyer Gold Posts: 286       Location: Russia, Perm | You first need to calculate basic air flow N/A. This is done by the formula. Basic air flow = V x rpm x 0.5 x E / 1000000 where, V - volume (cc), rpm - (6000) 0.5 - of 0.5 means that the four-stroke engine air in the cylinder comes only at the time of one turnover of the two. E - filling ratio (0.85). The number of 1000000 serves to convert cc to cubic meters. 2378 x 6000 x 0.5 x 0.85 /1000000 = 6.06 m3/min This is a basic air flow N/A 4G69 MIVEC engine. Remember this number. filling ratio for motors without systems (MIVEC, VTEC, VVTi) = 0.8 Edited by stayer 26/7/2012 15:40 | ||
| |||
| stayer |
| ||
 Frequent flyer Gold Posts: 286       Location: Russia, Perm | Now we need to calculate the required pressure. To do this, we use the formula. Rated power = the initial power x (the boost pressure /atmospheric pressure) Make an equation. 210 = 160 x ( X / 1 bar) 210 = 160 x X X = 210 / 160 X = 1.31bar (absolute pressure = atmospheric pressure + boost pressure For achievement of the power 210 hp need to 0.31 bar (4.5 psi) boost pressure | ||
| |||
| stayer |
| ||
 Frequent flyer Gold Posts: 286       Location: Russia, Perm | The next step is the calculation of the air flow with the turbocharged. This is done by the formula air flow turbo = boost pressure x basic air flow 1.31 x 6.06 = 7.94 m3/min To convert m3/min to a more correct term kg/min, m3/min should be multiplied by the density of the air at a height of geographic location (sorry, inscriptions in Russian) [IMG]http://i027.radikal.ru/1206/31/1a9886928f55.jpg[/IMG] (1a9886928f55.jpg) Attachments ---------------- 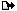 1a9886928f55.jpg (35KB - 742 downloads) 1a9886928f55.jpg (35KB - 742 downloads) | ||
| |||
| stayer |
| ||
 Frequent flyer Gold Posts: 286       Location: Russia, Perm | Now you can choose a turbocharger. We know the air flow. In the specification of turbochargers is, the parameter of consumption. It is expressed - kg per second. The weight of air per minute / 60 seconds = supply air (It is possible for English it sounds different) 7.94 / 60 = 0.13 kg per second Now I take the directory and find the desired me turbocharger I would like to say that in the metric system measure the speed of the flow kg/s. However, in the directories for the turbo this parameter is specified as lb/min. If you know of pressure and air flow (mass), you can find the turbine. To do this, open directory, for example Garrett Products | Turbochargers Now you need to select the turbocharger. I translated metric values its turbo. 0.13 kg/s = 17.2lb/min. As you remember absolute pressure = 1.31 bar Open performance map. We need to find a compressor to the intersection of lines air flow (17.2lb/min) and pressure (1.31 bar), were in the center of the oval. Thus, if I bought Garrett, then I would chose GT2560R. | ||
| |||
| Jump to page : 1 2 3 4 5 6 Now viewing page 1 [10 messages per page] |
| Search this forum Printer friendly version E-mail a link to this thread |
| (Delete all cookies set by this site) | |